Neonatal Jaundice
NICE Clinical guideline [CG98] Jaundice in newborn babies under 28 days. Last updated: Oct 2023.
Background Information
Classification
Physiological neonatal jaundice:
- >24 hours after birth
- Always unconjugated (indirect) hyperbilirubinaemia
- Typical duration
- <14 days in term babies (born ≥37 weeks)
- <21 days in preterm babies (born <37 weeks)
Pathological neonatal jaundice:
- Onset <24 hours after birth
- Can be either unconjugated (indirect) or conjugated (direct) hyperbilirubinaemia
- Typically causes prolonged neonatal jaundice
Prolonged neonatal jaundice:
- Duration
- >14 days in term babies (born ≥37 weeks)
- >21 days in preterm babies (born <37 weeks)
Causes (to be added)
Complications
Note that only unconjugated bilirubin can cross the blood-brain barrier:
- Severe unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia can result in:
- Acute bilirubin encephalopathy and/or
- Chronic bilirubin encephalopathy (aka kernicterus)
Conjugated bilirubin cannot cross the blood-brain barrier:
- Negligible neurotoxicity
- Main complications result from the underlying cause
Diagnosis Guidelines
Bilirubin Measurement
Timing
- Suspected/obvious jaundice < 24 hrs of life → measure within 2 hours
- Suspected/obvious jaundice ≥ 24 hrs of life → measure within 6 hours
Method of Measurement
There are 2 ways to measure bilirubin levels:
| Approach | Description | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Serum bilirubin | Gold standard method (most accurate):
|
|
| Transcutaneous bilirubin | Screening method:
|
|
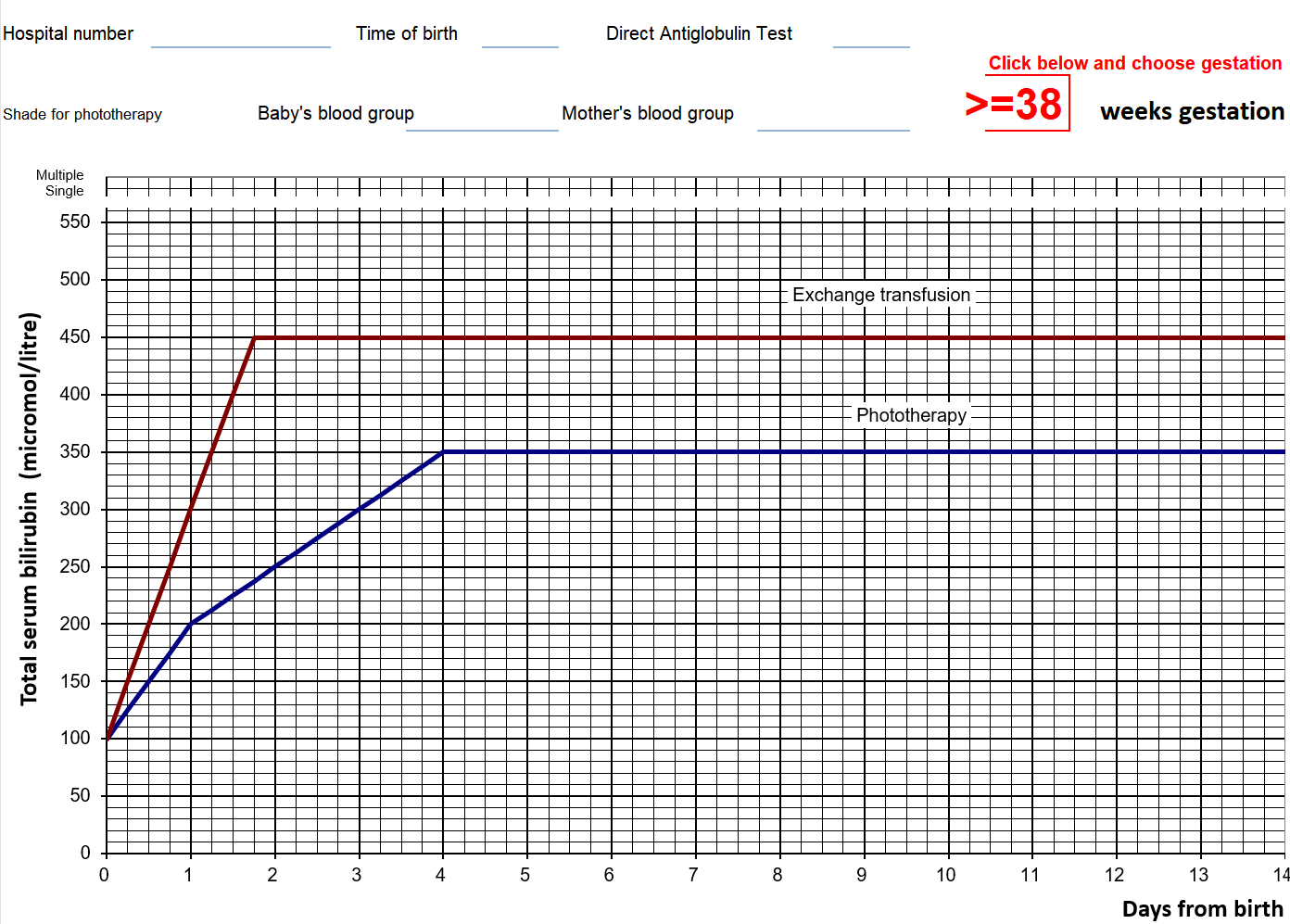
Serum bilirubin (NOT transcutaneous bilirubin), is used to guide management of neonatal jaundice.
Treatment graphs for phototherapy/exchange transfusion plot serum bilirubin against post-natal age (for 3 gestational age bands).
Investigating Underlying Cause (to be added)
Management Guidelines
Management
Reassure that breastfeeding, nappy‑changing and cuddles can usually continue
If on/above treatment line → offer corresponding treatment accordingly (i.e. phototherapy or exchange transfusion)
- If the bilirubin level is within 50 mmol/L below the phototherapy threshold → repeat bilirubin measurement
- Otherwise, no routine repeat measurement is required
Note that serum bilirubin level is used to guide management (NOT transcutaneous bilirubin).
Example of a treatment threshold graph (exam questions always provide this table, and the thresholds depend on gestational age):
Phototherapy
Phototherapy should be given using an artificial light source (not natural sunlight)
Educate parents about phototherapy:
- Eye protection required
- Increased risk of dehydration
- Short breaks for feeding, nappy changes, and cuddling are encouraged
- Bronze baby syndrome is a rare but benign condition
Monitoring
Monitoring during phototherapy:
- Repeat 4-6 hours after initiating phototherapy
- Repeat every 6-12 hours when the serum bilirubin level is stable / falling
Monitoring after phototherapy:
- Repeat 12-18 hours after stopping phototherapy (to detect potential rebound)
Stopping Phototherapy
Only stop phototherapy when:
- Serum bilirubin level is at least 50 mmol/L below the phototherapy threshold
Intensified Phototherapy
Phototherapy can be intensified by adding another light source or increasing the irradiance of the initial light source
Consider if:
- Serum bilirubin level is rising rapidly (>8.5 mmol/L per hour), or
- Poor response (bilirubin continues to rise/does not fall within 6 hours of initiating), or
- Serum bilirubin is within 50 mmol/L below the threshold for exchange transfusion after 72 hours since birth
IV immunoglobulin can be used as an adjunct to intensified phototherapy. Indication:
- Rhesus or ABO haemolysis (i.e HDN), AND
- Bilirubin rising at a rate of >8.5 micromol/L/hr
Exchange Transfusion
Exchange transfusion should be performed in an intensive care bed
- Use a double volume exchange transfusion
- Do not stop any ongoing phototherapy